ENTHEOGENS
Entheogens (from the Ancient Greek entheos ["god", "divine"] and genesthai ["generate" - "generating the divine within"]) are psychoactive substances, typically of plant origin, that are used in religious, ritual, or spiritual contexts. Listed below are some of the more common psychedelic entheogens.
Psilocybin
Psilocybin mushrooms are a family of psychoactive mushrooms that contain the psychedelic tryptamines psilocin and psilocybin. Psilocybin mushrooms occur on all continents and consist of more than 200 species, the most potent of which belong to the genus Psilocybe.
Psilocin, 4-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (active metabolite of psilocybin)
Psilocybin mushrooms. Image: Alan Rockefeller
DMT
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (also known as DMT, N,N-DMT and "The Spirit Molecule") is a classical psychedelic substance of the tryptamine class. Despite being one of the simplest psychedelic compounds, it is known for its unique ability to produce short-lived but intense visionary states and complete hallucinations.
5-MeO-DMT
5-Methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (commonly known as 5-MeO-DMT) is a naturally occurring psychedelic substance of the tryptamine class. It is distributed in a wide variety of plant species, as well as in the venom of a single psychoactive toad species (Bufo Alvaris).
Bufo Alvaris toad
Peyote buttons
Mescaline
3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenethylamine (also known as mescaline) is a naturally-occurring classical psychedelic substance of the phenethylamine class. It occurs naturally in the peyote cactus (Lophophora williamsii), and a number of other cacti species such as the Echinopsis pachanoi (San Pedro cactus) and Echinopsis peruviana (Peruvian Torch).
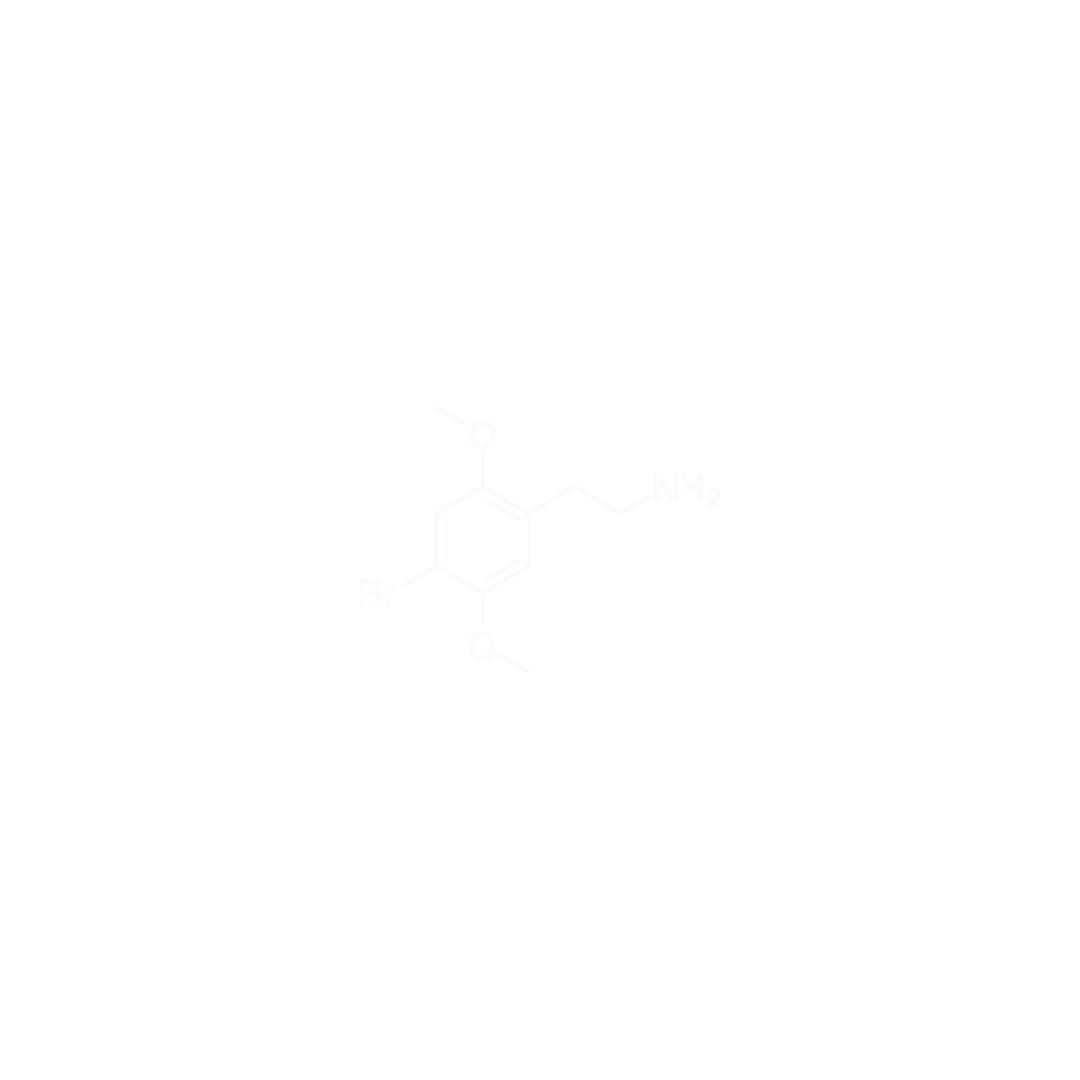
2C-B
4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (also known as 2C-B) is a psychedelic substance of the phenethylamine class. 2C-B is the most popular member of the 2C-x family of psychedelic phenethylamines, which are closely related to the classical psychedelic mescaline. 2C-B was a favourite of the famous psychedelic chemist Alexander Shulgin.
Alexander Shulgin
Bottle and tabs of LSD
LSD
Lysergic acid diethylamide (also known as LSD, LSD-25, Lucy, and Acid) is a classical psychedelic substance of the lysergamide class. It is considered to be the the best known, most researched, and culturally influential psychedelic substance.
Ayahuasca
Ayahuasca (pronounced /eye-uh-WAHS-kuh/ and also known as Yagé) is an umbrella term that refers to a wide variety of traditional and modern brews and infusions of natural plant sources that produce powerful psychoactive effects. Of these, it most commonly consists of a DMT-containing plant source in combination with one that contains an MAOI or RIMA (typically sources like B. caapi vine or Syrian Rue) to produce uniquely potent psychedelic effects.
Preparing ayahausca
Salvia divinorum
Salvia
Salvia divinorum (also called Diviner's Sage, Ska María Pastora, Seer's Sage, and Salvia) is a psychoactive plant in the Salvia genus. Its native habitat is within Cloud Forest in the isolated Sierra Mazateca of Oaxaca, Mexico where it grows in shady and moist locations. The plant grows to over a meter high and has hollow square stems, large leaves, and occasional white flowers with violet calyxes. Salvia divinorum is the only known natural source of Salvinorin A, the main psychoactive molecule within the plant.
Iboga
Tabernanthe iboga, or simply iboga, is a perennial rainforest shrub and psychedelic which is native to western Central Africa. In parts of Africa where the plant grows, the bark of the root is chewed for various pharmacological or ritualistic purposes. Ibogaine, the active alkaloid, is also used to treat substance abuse disorders and depression.
Tabernanthe iboga
The cannabis plant
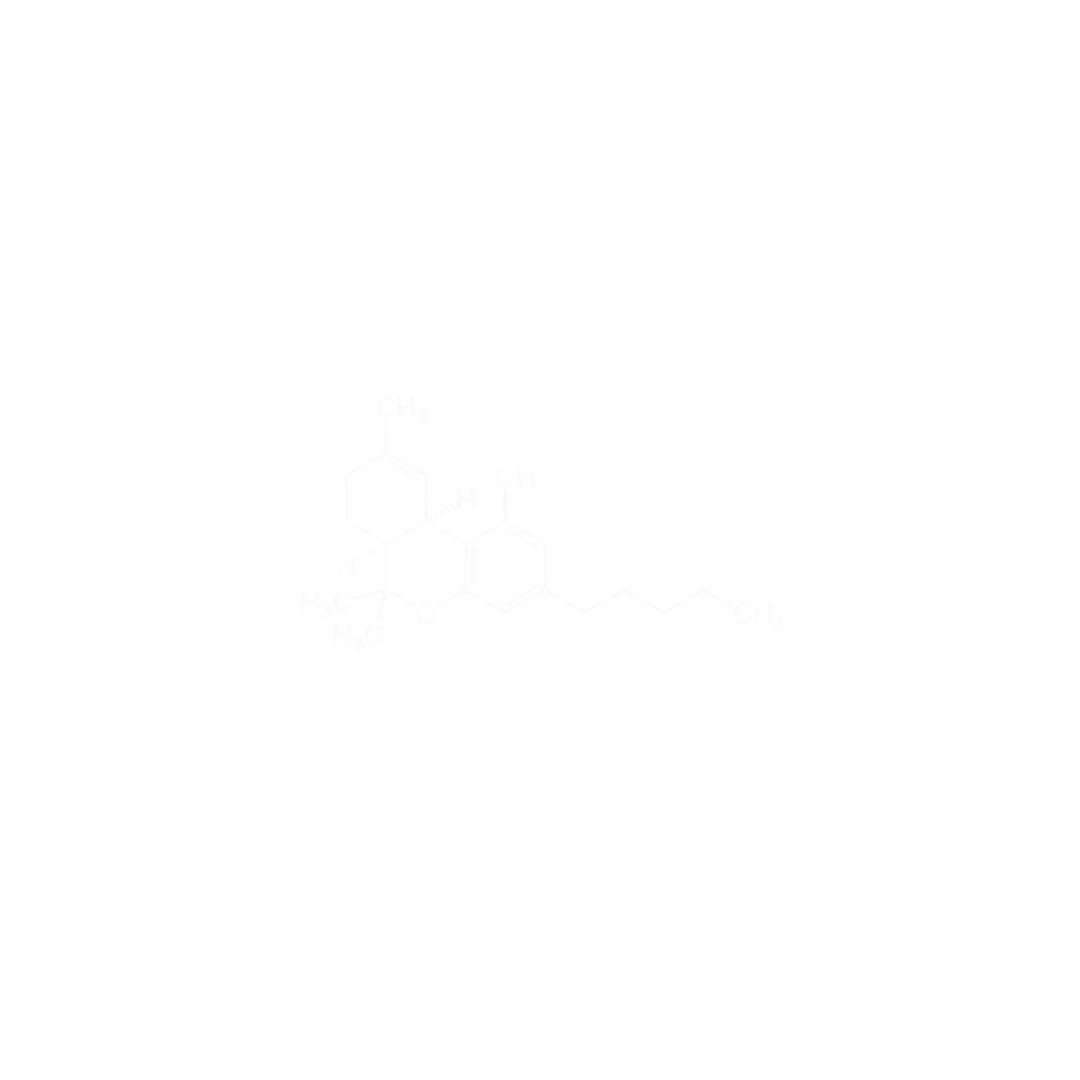
Cannabis
Cannabis (also known as marijuana, weed, pot, grass and herb) is a preparation of the cannabis plant that produces psychoactive effects when consumed (via smoking, vaporizing, or ingestion), including some psychedelic effects. The principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which makes up one of 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 84 other cannabinoids such as cannabidiol (CBD), cannabinol (CBN), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), and cannabigerol (CBG).
MDMA
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (also known as Ecstasy, E, Molly, Mandy, and MDMA) is a classical entactogen substance of the amphetamine class with some psychedelic effects. It is considered to be the prototypical entactogen, a diverse group of substances that includes MDA, methylone, mephedrone, and 6-APB. It primarily acts by increasing the activity of the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain.
MDMA crystals
Ketamine in liquid and crystal form
Ketamine
Ketamine (also known as ket and K) is a classical dissociative substance of the arylcyclohexylamine class with some psychedelic effects. It is one of the most well-known and widely-used dissociatives, a diverse group that includes phencyclidine (PCP), methoxetamine (MXE), dextromethorphan (DXM), and nitrous oxide. Today, ketamine is widely used in human and veterinary medicine, primarily for general anesthesia for surgical procedures.